Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) is a water-soluble B vitamin present naturally in various foods and available as a supplement. In general, vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid help to metabolize or convert proteins, carbohydrates, and fats you eat from food into energy. It also maintains our healthy skin, hair, and eyes. Pantothenic acid is one of the B vitamins that is synthesized from amino acids β-alanine and pantoic acid. Unlike vitamin E or vitamin K, it occurs in only one chemical form pantothenic acid.
Benefits of Pantothenic Acid
Vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid is a starting compound for the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA), a cofactor for many enzymes that control various biological processes.
The main benefits of vitamin B5 may include:
- Metabolizes food into energy
- Supports in cardiovascular health
- Maintain healthy skin
- Maintain healthy hair
- Making red blood cells or hemoglobin that carry oxygen throughout the body
- Proper functioning of the nervous system
- Improves mental performance
- Helps to control your body’s stress
Metabolizes Food into Energy
All B vitamins help to convert carbohydrates into glucose which is used for the production of energy in your body.
All animals require vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) in order to synthesize coenzyme A (CoA) which is essential for fatty acid metabolism. Taking vitamin B5-containing foods and supplements may lower your body weight by activating lipoprotein lipase and an enzyme that burns fat cells.
It also synthesizes and metabolizes proteins and carbohydrates in your body. Therefore, regularly eating foods and supplements that contain a high level of vitamin B5 may help your metabolism function at optimal levels.
Various studies show that vitamin B5 reached foods and supplementation help in reducing cholesterol levels in people who suffer from dyslipidemia.
Supports in Cardiovascular Health
The high serum concentration of LDL cholesterol is a major risk factor for coronary heart disease. Various studies have shown that the derivative of vitamin B5, pantethine may help to reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglyceride levels in your blood. In a similar fashion, it raises HDL (good) cholesterol levels in your blood.
A daily dose of 900 milligrams of vitamin B5 has been shown to lower LDL (bad) cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. Therefore, vitamin B5 reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease.
900 mg is significantly higher than the recommended daily dose of vitamin B5. Therefore, it is highly recommended to intake under the supervision of your doctors or medical professionals.
Pantothenic Acid for skin
Pantothenic acid and Panthenol are best known for their hydrating, soothing, and moisturizing abilities. Various types of research suggest that pantothenic acid can be used on the skin to relieve itchiness and promote healing caused by eczema, diaper rash, poison ivy, and insect bites.
Unlike other common moisturizing ingredients like hyaluronic acid, panthenol has the added advantage of acting as both a humectant and an emollient. Humectants bind water in your skin, while emollients seal in the cracks in the skin, keeping that water locked in. Therefore, it helps to maintain softness and elasticity in your skin.
- Along with great moisturizing properties, it also activates the production of cells that are essential for wound healing.
- Panthenol-containing skincare products are also useful for strengthening your skin barrier or the outermost layer of your skin that plays an essential role in keeping harmful toxins and irritants out, and moisture locked in.
- The anti-inflammatory action of vitamin B5 and panthenol protects your skin from UV-induced redness.
- Various studies show that vitamin B5 reached foods and supplements may beneficial to the reduction of acne outbreaks compared to those who didn’t take this vitamin.
Vitamin B5 for hair
A form of vitamin B5, calcium pantothenic acid is a vital ingredient for your healthy hair. It strengthens and nourishes your hair follicles to promote healthy hair growth and prevent hair loss.
Pro-vitamin B5 or panthenol has been used widely in many hair care formulas. A study suggests that panthenol is effective for the treatment of androgenic alopecia, the most common hair loss problem in both men and women. It also boosts cellular repair activity in hair follicles and strengthens hair structure and prevents brittleness and breakage.
Helps Create Red Blood Cells
Creating red blood cells is another benefit of vitamin B5. It enhances the level of iron-containing oxygen-transport protein or hemoglobin in our bodies. Therefore, it is beneficial for the treatment and prevention of anemia.
Maintains Healthy Nerve Function
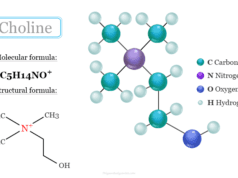
Like vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), and vitamin B12 (cobalamin), vitamin B5 also helps to maintain healthy nerve function. It helps to create an important molecule called acetylcholine that sends nerve signals to your immune system, heart, lungs, kidneys, liver, and more.
It is also used to send nerve signals to your muscles. Therefore, the primary signs of B vitamins deficiency are muscle impairment and pain. It creates a condition known as burning feet syndrome. It occurs when a person experiences a lack of feeling in the feet along with painful burning, inflammation, and the feeling of ongoing fatigue and weakness.
Improves Mental Performance
Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) is an essential substrate for the synthesis of coenzyme A (CoA). Beyond its role in oxidative metabolism, coenzyme A (CoA) also helps to improve the structure and function of brain cells.
Pantothenic acid via CoA is involved in the synthesis of multiple neurotransmitters and steroid hormones in your body. Therefore, obtaining proper amounts of B vitamins including B5 may be able to prevent memory loss, migraine headaches, chronic brain syndrome, depression, motion sickness, insomnia, and alcohol dependence.
Helps to Control your Body’s Stress
People who are chronically stressed or who are dealing with adrenal fatigue symptoms are highly encouraged to intake B vitamins in their daily foods and supplements. It may help to reduce chronic stress and control appetite, energy, mood, temperature, etc.
Vitamin B5 is partially responsible for regulating adrenal function by creating the stress hormone cortisol. Various studies show that pantothenic acid supplementation stimulates the ability of adrenal cells and participates normal production of cortisol. These are important to maintain your motivation and concentration.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) in Foods
Some amount of vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid is found in nearly every plant and animal food. The name pantothenic acid derives from the Greek word pantos meaning found everywhere in nearly every food.
The best animal-based food sources of vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) may include:
| Animal-based food | Amount (mg) |
| Beef liver, boiled, 3 ounces | 8.3 |
| Roasted chicken, breast meat, 3 ounces 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Tuna, fresh, bluefin, cooked, 3 ounces | 1.2 |
| Milk, 2% milkfat, 1 cup | 0.9 |
| Egg, hard-boiled, 1 large | 0.7 |
| Greek yogurt, vanilla, nonfat, 5.3-ounce container | 0.6 |
| Cheese, cheddar, 1.5 ounces | 0.2 |
The best plant-based food sources of vitamin B5 or pantothenic acid may include:
| Plant-based food | Amount (mg) |
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | 5.0 |
| Shitake mushrooms, cooked, ½ cup | 2.6 |
| Sunflower seeds, ¼ cup | 2.4 |
| Avocados, raw, ½ avocado | 1.0 |
| Mushrooms, white, stir-fried, ½ cup | 0.8 |
| Potatoes flesh, and skin, baked, 1 medium | 0.7 |
| Peanuts, roasted in oil, ¼ cup | 0.5 |
| Broccoli, boiled, ½ cup | 0.5 |
| Medium grain Brown rice, cooked, ½ cup | 0.4 |
| Oats, cooked with water, ½ cup | 0.4 |
| Carrots, chopped, raw, ½ cup | 0.2 |
| Tomatoes raw or sliced, ½ cup 0.1 | 0.1 |
Whole grains are another good source of this vitamin but milling may remove pantothenic acid because it is found in the outer layers of whole grains.
Various analytical techniques are used to gain information on pantothenic acid content in foods. Older data on food composition was based on microbiological analysis but recently high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is used to analyze pantothenic acid in foods prepared for infants.
Dietary recommendations for Vitamin B5
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM) updated Estimated Average Requirements (EARs) and Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) for B vitamins. It found that the data was insufficient to derive an EAR and RDA for vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid). Therefore, Adequate Intake (AI) was established for all ages based on usual pantothenic acid intakes in healthy people.
The daily requirements of vitamin B5 are different for different age groups such as infants, children, and elderly people. The current AI of pantothenic acid for ages 14 and up is 5 mg/day.
| Age group | Age | Adequate intake (mg) |
| Infants | 0–6 months | 1.7 |
| 7–12 months | 1.8 | |
| Children | 1–3 years | 2.0 |
| 4–8 years | 3.0 | |
| 9–13 years | 4.0 | |
| Adult men and women | above 14 years | 5.0 |
| Pregnant women | 6.0 | |
| Breastfeeding women | 7.0 | |
No adverse side effects on oral dosages of pantothenic acid are found in humans or animals. Therefore, Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) cannot be derived for this vitamin.
Pantothenic Acid Supplements
Pantothenic acid or vitamin B5 is an essential nutrient that is naturally present in various foods. It may available in multivitamins and B complex vitamins or sold separately under dietary supplements of pantothenic acid and calcium pantothenate. Vitamin B5 is available in a variety of forms such as tablets, soft gels, and capsules.
Best Vitamin B5 Supplements
Most people get enough pantothenic acid or vitamin B5 from their daily food sources because it is found in a variety of foods that we intake daily. Usually, vitamin B5 deficiency is observed in people who have a genetic mutation where pantothenic acid cannot be metabolized. Apart from this, malnourishment also causes B5 deficiency.
The supplementation is always safe for most cases but always ask a doctor or healthcare professional before taking B5 or pantothenic acid supplements. You can purchase pantothenic acid supplements in capsules, chewable gummies, and tablet forms.
Some best supplements of vitamin B5 and their comparison and cost are listed below in the table,
| Brand | Item | Form | Biotin dosage | Cost per bottle |
| Jarrow Formulas | Jarrow Formulas Pantothenic Acid B5 500 mg | Capsule | 500 mg | around $25 |
| Now Foods | NOW Supplements, Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B-5) 500 mg, B-Complex Vitamin, 250 Capsules | Capsule | 500 mg | around $18 |
| Best Naturals | Best Naturals Pantothenic Acid 500 mg 120 Tablets | Tablet | 500 mg | around $10 |
| Life Extension | Life Extension Pantothenic Acid 500 mg | Capsule | 500 mg | around $11 |
Vitamin B5 Deficiency
As already mentioned, vitamin B5 deficiency is extremely rare in the United States and other developed parts of the world because it is found in almost all foods that we eat. Therefore, with a proper diet, most people get their daily required B5 from naturally occurring foods they eat.
Pantothenic acid deficiency can be found in people who suffer from acute malnutrition or severe alcoholism. When someone has a pantothenic acid deficiency, they may also be suffering from several other vitamin deficiencies. Therefore, it is difficult to identify the effects of this specific vitamin deficiency.
Generally, vitamin B5 deficiency does not cause any diseases but it is used in the treatment of several health conditions. The deficiency symptoms are infrequent for most people. The common signs and symptoms of a vitamin B5 deficiency may include:
- Burning feet
- Fatigue
- Depression, disturbed sleep, and headache
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Stomach pain and Upper respiratory infections
- Vomiting
- Muscle cramps
Usually, vitamin B5 deficiency is caused by a genetic mutation and malnourishment where pantothenic acid cannot be metabolized in your body.