List of Peptides and What They Do?
Peptides are a continuous and unbranched list of amino acid biopolymers joined together by peptide bonds. A list of peptides in our body can do a wide spectrum of biological functions in cells. The most common benefits of collagen peptides and other peptide supplements are skin care, muscle growth, and fat loss. Polypeptides are the basic building blocks or smaller versions of proteins and the monomeric units of peptides are amino acids. We can commonly differentiate peptides from a protein molecule by their structure or shorter amino acid chain length. Foods that naturally contain amino acids or proteins are good sources of peptides. Collagen peptides and peptide hormones are important biomolecules in our body that uses to control various biological activities such as bodybuilding, skincare, and weight loss.
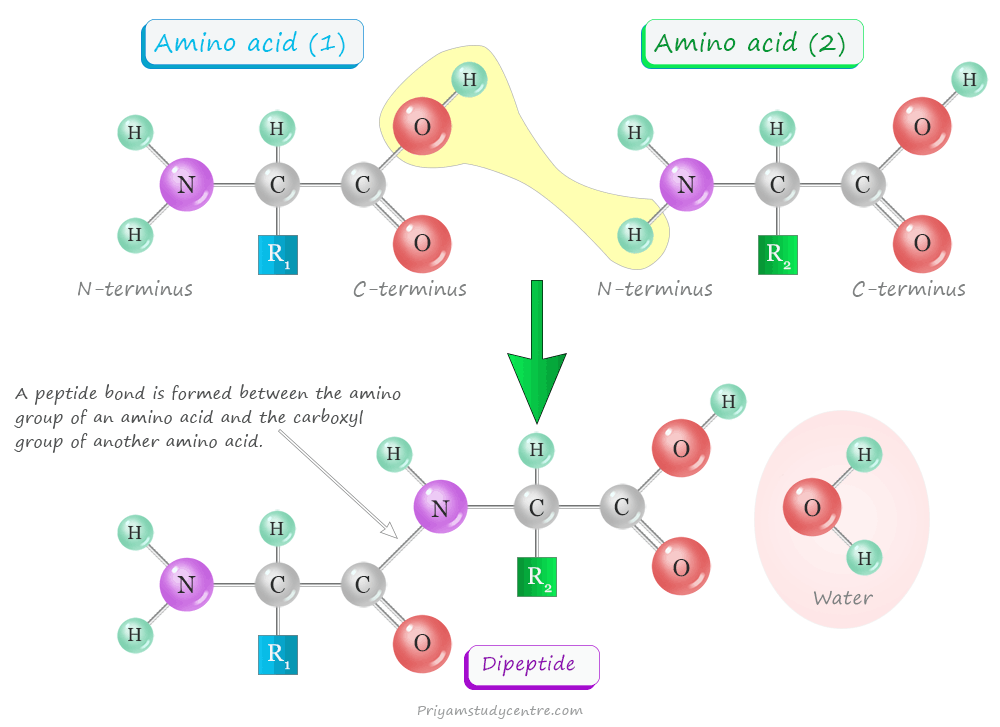
A peptide bond is formed when the amino group of an amino acid combines with the carboxyl group of another amino acid. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl group) in their structure. Proteins and polypeptides are long molecules made up of multiple peptide subunits.
A dipeptide will have two amino acids with one peptide bond. However, a polypeptide will have more than 10 amino acids with many peptide links. Proteins are also polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more.
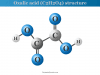
Peptide Bond Structure
The peptide bonds in peptides are rigid and planar because the atoms in the -CONH- group are planar and oxygen and hydrogen are in the trans-position. The C-N bond length (1.32 Å) is shorter than the usual C-N bond length (1.47 Å). Therefore, the peptide bond has a partial double bond charterer. The -C=O and -NH groups in peptide bonds are polar and are involved in hydrogen bond formation.
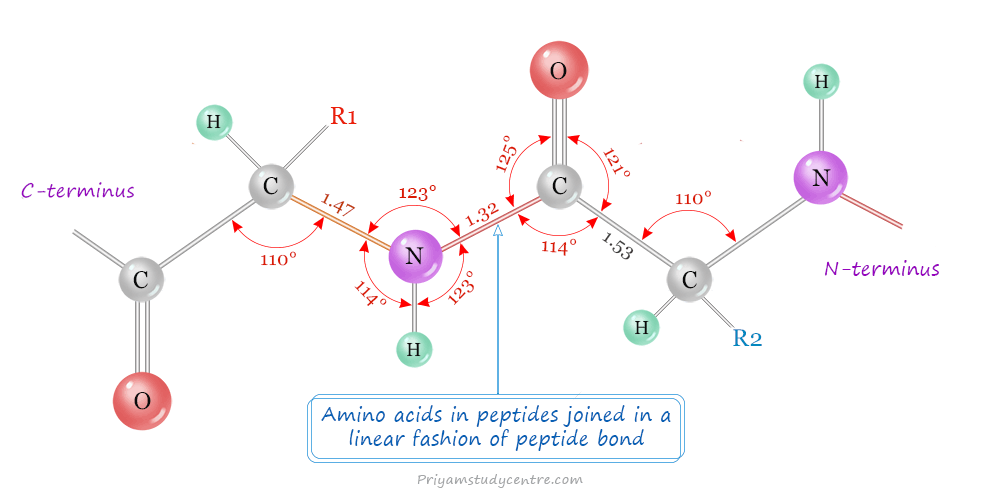
A peptide molecule is formed by a condensation reaction between various amino acids. Each amino acid in a peptide is called a residue. Because a double bond is shorter and stronger. Therefore, more free energy is required for breaking the peptide bond.
When peptides are hydrolyzed by acids, alkalis, or enzymes, they form a mixture of amino acids. It suggests that amino acids in proteins joined in a linear fashion of peptide linkages. The carboxyl group of one amino acid combines with the amino group of the next amino acid. A list of peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl group) in their structure.
For naming peptides, the amino acids suffix -ine (glycine), -an (tryptophan), -ate (glutamate) are changed to -yl with the exception of C-terminal amino acids. For example, a tripeptide composed of an N-terminal glutamate, cysteine, and a C-terminal glycine is named glutamyl-cysteinyl-glycine.
List of Peptides
A list of peptides in our body and other living organisms can do a wide spectrum of biological functions such as skin care, bodybuilding, and weight loss. The common examples of peptides that do various biological activities are:
- Collagen peptides
- Glutathione
- Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
- Oxytocin
- Vasopressin
- Angiotensin
- Methionine enkephalin
- Bradykinin and kallidin
- Peptide antibiotics
- Aspartame
- Gastrointestinal hormone
- Lethal peptides
Proteins, peptides, and hormones are important biomolecules that do a list of biological activities in the cells of living organisms. A list of peptides and what they do in living cells are discussed below:
Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides formed when collagen protein breaks down into smaller pieces. It is the main structural protein and the main component of connective tissues. It also makes up several body parts such as cartilage, bone, and skin. Therefore, it is beneficial for our skin and strengthening our bones.
We can get collagen from foods like pork skin and bone. Collagen supplements have also become popular for improving skin health. Most of the supplements are obtained in hydrolyzed form which means the collagen has been broken down into college peptides for easier to absorb. The peptide supplements of collagen come primarily in powder form but are also available in capsules.
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide formed by three amino acids glycine, cysteine, and glutamic acid. It is produced by the liver and exists in reduced and oxidized form. The reversible oxidation-reduction of glutathione is very important for many biological functions.
- It acts as a coenzyme for certain enzymes like postaglandin synthetase, glyoxalase, etc.
- Glutathione is essential for the functioning of several proteins because it prevents the oxidation of sulfhydryl groups of several proteins.
- The reduced form of glutathione maintains the RBC membrane structure and integrity.
- Glutathione may protect the hemoglobin from oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
- In the intestine and kidney, it helps to transport several amino acids.
- Glutathione may involved in the detoxification process in which toxic substances are converted to mercapturic acids.
- Toxic amounts of peroxides and free radicals produced in the cells are scavenged by the selenium-containing enzyme glutathione peroxidase.
Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH)
Acid hydrolysis of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone gives three amino acids, histidine, glutamic acid, and proline. Therefore, the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a tripeptide secreted by the hypothalamus. It stimulates the pituitary gland to release the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) that plays a critical role in development, growth, and cellular metabolism.
The TSH peptide is an important regulator that regulates the level of thyroid hormone and it is a major center of neural control in the endocrine system. Therefore, it controls physiological responses to the external and internal environment.
Oxytocin Peptide
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone that contains 9 amino acids arranged in a cyclic form and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. It is also secreted from other tissues such as the ovaries and testes in the human body.
Oxytocin is extracted from the gland by acetic acid and purified by chromatography or electrophoresis. The isoelectric point of oxytocin is 7.7. The value suggests the presence of a free amino group but no free carboxyl group.
Oxytocin commonly helps in the construction of the uterus. The social neuropeptide, oxytocin is a love hormone because it plays a key role in promoting maternal behavior and mother-infant bonding in mammals.
Vasopressin Peptide
Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is a nonapeptide produced by the posterior pituitary gland. It stimulates the kidneys to retain water and increases the blood pressure.
Angiotensins
Angiotensin I is a decapeptide (10 amino acids) converted to angiotensin II (8 amino acids) and helps to regulate blood pressure and fluid balance in our body. Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal gland of our body.
Methionine Enkephalin
Methionine enkephalin (MENK) is an opioid pentapeptide found in the brain and it controls various biological activities. This pentapeptide has been found mainly in the adrenal medulla and throughout the central nervous system (CNS).
Methionine enkephalin commonly inhabits the sense of pain in the human body. It is also the endogenous ligand of the opioid growth factor that plays a vital role in the regulation of tissue growth and regeneration.
Bradykinin and Kallidin
Bradykinin and Kallidin are nona and decapeptides that help to regulate blood pressure, inflammation, coagulation, and pain. These peptides can be produced from plasma proteins by snake venom enzymes.
Peptide Antibiotics
Peptide antibiotics are a class of microbial antibiotics that have anti-infective and antitumor properties. Examples of peptide antibiotics are bacitracin, colistin, polymyxin B, gramicidin, tyrocidin, actinomycin, etc. They are used widely in medicine, food, animal husbandry, agriculture, and aquaculture.
Chemically, bacitracin contains non-protein polypeptide chains that inhibit cell wall synthesis and are active against gram-positive bacteria.
Aspartame
Aspartame is a dipeptide formed by the combination of aspartic acid and phenylalanine. It is about 200 times sweeter than the common sweetener sucrose. Therefore, only a tiny amount of aspartame peptide is necessary to sweeten foods and drinks.
Aspartame is used widely for making low-calorie artificial sweeteners and soft drinks. Most studies show that the use of aspartame peptide is safe for most people.
Gastrointestinal Peptides
The gastrointestinal peptides are the list of hormones secreted by enteroendocrine cells in the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine in the human body. They control various biological functions of the digestive organs of the human body.
Examples of gastrointestinal peptides are gastrin, secretin, somatostatin, ghrelin, bombesin, etc. They commonly serve as hormones and regulate the physiological activity of the pancreas and intestine.
Lethal Peptides
Bacterial peptides namely microcystin and nodularin promote hepatic tumors in small doses while in large doses they are lethal. Such types of peptides can be found commonly in the venom of snakes, scorpions, sea anemones, and cone snails. Lethal toxins have been isolated from venom by liquid chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography.
Peptides Sources
Peptides are the smaller version of proteins and polypeptides. Therefore, peptides are formed during various biological processes in the human body and other living organisms. They are also created artificially in biochemical laboratories.
Foods that naturally contain amino acids or proteins are good sources of peptides. Therefore, peptides can be found in many protein reached foods foods such as meat, fish and shellfish, beans and lentils, soy, oats, hemp seeds, etc.
Benefits of Peptides
Peptides can control various biological activities in the human body. However, in many cases, they served as a hormone. For example, insulin is a hormone that contains 51 amino acids and it promotes glycogenesis in cells or it converts glucose into glycogen.
The most common benefits of peptide supplements are skin care, muscle growth, and fat loss. Insulin was the first peptide ever made in a lab by scientists and it is called a synthetic peptide. It has also been used to treat people with type 1 diabetes since 1923.
Our body makes different types of peptides and each of them has definite biological benefits. Scientists also made many peptide molecules in the laboratory and they are used as supplements to treat various health diseases.
Benefits of Collagen Peptide
For a long time, various companies have used a list of peptides in their skin care products. Collagen is the main structural protein that is the main component of connective tissues and makes up several body parts such as cartilage, bone, and skin. Therefore, it is beneficial for our skin and strengthening our bones.
The food and supplements that contain collagen peptides provide a variety of health benefits. The most common health benefits of collagen peptides are:
- Improve skin health: Collagen peptides may help strengthen the skin by improving elasticity and hydration.
- Relieve joint pain or improve bone loss: Some studies show that collagen peptide supplements may help improve osteoarthritis or bone loss and reduce overall joint pain in aged people.
- Boost muscle mass: Collagen is an important component of muscle skeleton. Therefore, the supplemental form of collagen peptides may boost your muscle mass.
- Maintain heart health: Collagen is an important protein that helps to maintain heart health because without enough collagen, arteries may become less flexible and elastic.
- Strengthen hair and nails: Some research shows that peptides form of collagen may strengthen your hair and nails.
- Improve brain health: The peptide form of collagen may improve your brain health by reducing anxiety symptoms.
- Help to support weight loss: The peptide form of collagen may help to support weight loss at a faster rate of metabolism.
Peptides for Bodybuilding
Peptides are naturally occurring biological molecules that play critical roles in muscle growth and bodybuilding. Growth hormones are a list of peptides that can play critical roles in bodybuilding because they can stimulate the production and release of human growth hormones.
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a tripeptide secreted by the hypothalamus in our body. It stimulates the pituitary gland to release the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). It plays a significant role in bodybuilding through development, growth, and cellular metabolism by promoting the loss of body fat.
Peptides for Fat Loss and Muscle Gain
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a tripeptide secreted by the hypothalamus and helps in fat loss and muscle gain. It stimulates the pituitary gland to release the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) that plays a critical role in development, growth, and cellular metabolism.
Hexarelin is also a synthetic growth hormone-releasing peptide used to build muscle, burn fat, and increase overall energy levels.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Peptides?
Peptides are a continuous and unbranched list of amino acid biopolymers joined together by peptide bonds. They are the smaller version of proteins and are beneficial for our health because they are more easily absorbed by our body than proteins.
A list of peptides are formed in our body during various biological functions. Due to potential health benefits, peptide supplements are used for pro-aging support, anti-inflammatory actions, and muscle-building.
What do Peptides Do?
Peptides are structurally similar to a list of hormones and messaging compounds in our body. Therefore, they control various biological activities in our bodies.
Depending on sequence and composition, certain peptides in our body may help to boost our imino system, protect cells against damage, be beneficial for our skin and strengthen our bones, prevent blood clots, and reduce cholesterol, inflammation, and blood pressure.
For example, collagen peptides provide a variety of health benefits such as improving skin health, reducing joint pain or improving bone loss, boosting muscle mass, maintaining brain and heart health, and may help to support weight loss.
How to Take Collagen Peptides?
Collagen is the main structural protein that is the main component of connective tissues and makes up several body parts such as cartilage, bone, and skin. Therefore, it is beneficial for our skin and strengthening our bones.
Our body does not absorb collagen protein directly. Therefore, most of the supplements containing collagen are in hydrolyzed form which means the collagen has been broken down into college peptides for easier to absorb.
We can take collagen peptides in the form of pills or capsules. It is also taken by mixing collagen peptide powder into smoothies, shakes, soups, or water.
What are Peptides Used For?
Peptides may be easier to absorb by our body than proteins because they are smaller versions of proteins. Therefore, therefore beneficial for our health and is used mainly due to pro-aging support, anti-inflammatory, or muscle-building properties. Due to the potential health benefits, many peptide supplements are available and manufactured from food or made synthetically in biochemical laboratories.
In medicine, peptides are used for making various pharmaceuticals to treat health diseases. Many peptides are obtained from food or made synthetically for skin and hair care products by strengthening skin and hair. Many synthetic and natural peptides are also used for preventing virus replication, relieving joint pain or improving bone loss, boosting muscle mass, maintaining heart and brain health, and helping to support weight loss.
Why are Peptides Important?
Peptides are important because they are the basic building blocks of many proteins, hormones, and enzymes that control various biological activities in our body.